Elicitations
Overview
Elicitations allow MCP servers to request structured input from users during tool execution. This enables interactive workflows where servers need additional information mid-operation.
Key Capabilities
🔔 Server-initiated modal
Server-initiated modal dialogs during tool execution
📝 Supports multiple types
Support for Boolean, Number, String, and Enum input types
📅 mart input fields
Smart input fields (email, date, datetime, URI validation)
📋 Dedicated Elicitations tab
Dedicated Elicitations tab for pending requests
📜 Complete history
Complete history with status tracking
⏱️ Configurable timeout
Configurable timeout behavior (optional)
✅ Accept/Reject workflow
User can Accept/Reject to determine process
How Elicitations Work
Typical Flow
- User calls a tool (from Tools tab or via Chat)
- Server needs input (e.g., “Approve this action?”)
- Modal appears with the server’s message and input fields
- User responds by filling fields and clicking Accept/Reject
- Server receives response and continues execution
Server-Initiated Requests
Modal Dialog
When a server requests input during execution, a modal automatically appears.
Modal contents:
- Server’s message/question
- Input fields based on requested schema
- Accept and Reject buttons
📸 Screenshot:
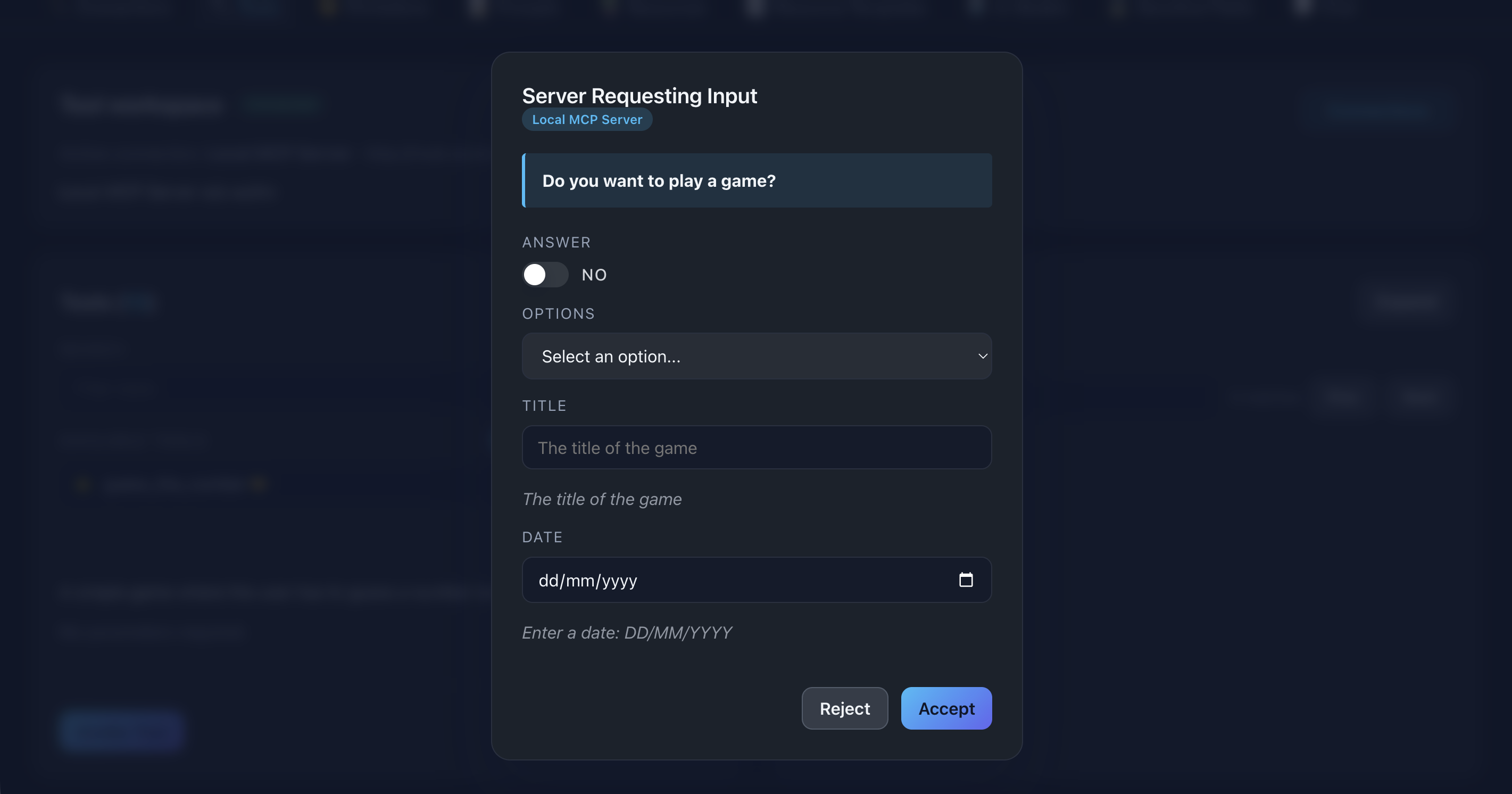
Description: Show the elicitation modal with a server message and input fields visible
Input Types
Boolean
Display: Toggle switch with Yes/No labels
Use case: Confirmations, approvals
Example: “Approve this operation?”
📸 Screenshot:
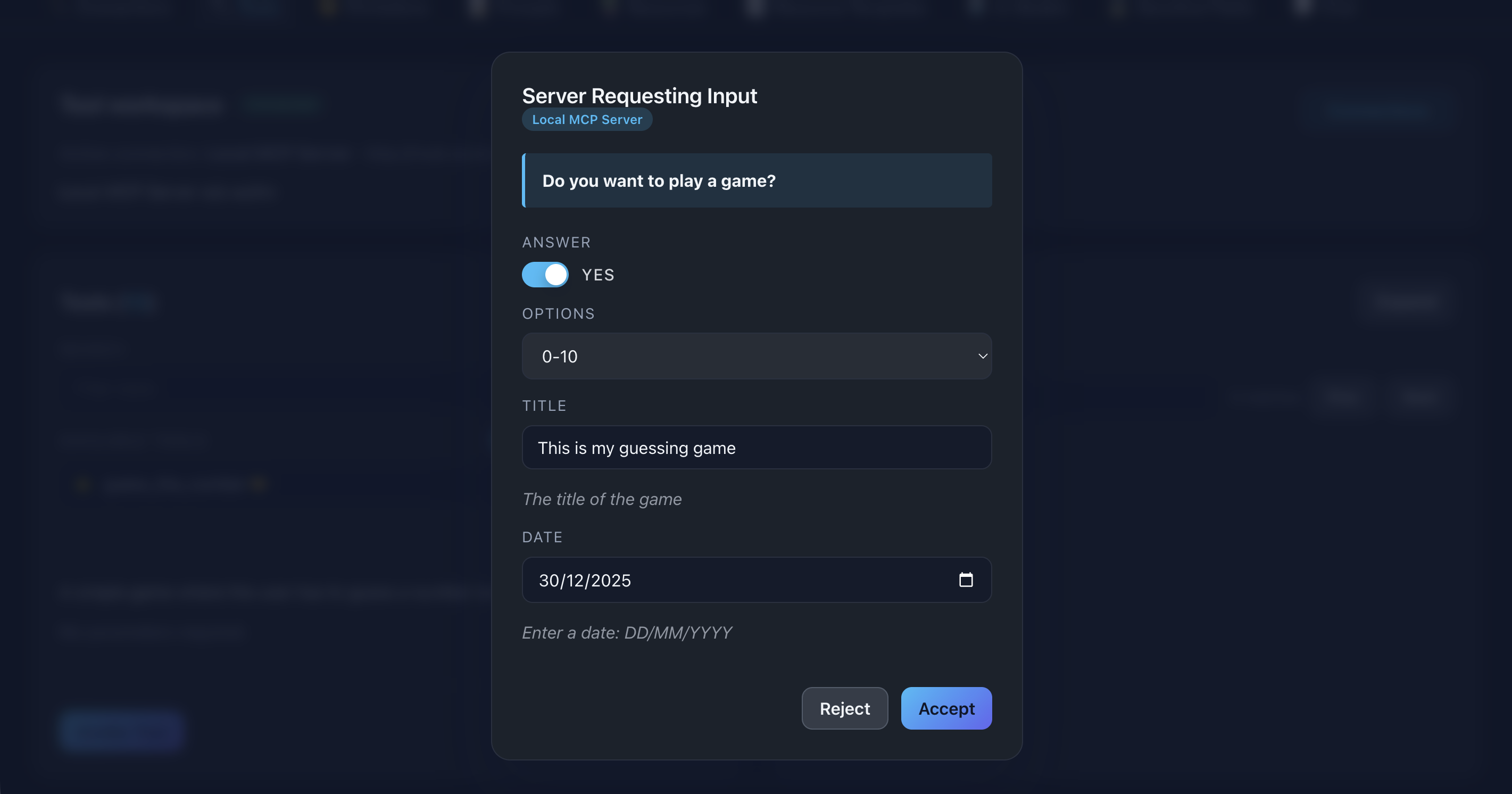
Description: Show a boolean toggle switch in an elicitation form
Number
Display: Numeric input field
Use case: Quantities, thresholds, timeouts
Example: “Enter timeout in seconds”
String
Display: Smart input adapting to format
Formats:
- email: Email input with validation
- date: Date picker
- datetime: DateTime picker
- uri: URL input with validation
- text (default): Standard text input
📸 Screenshot:
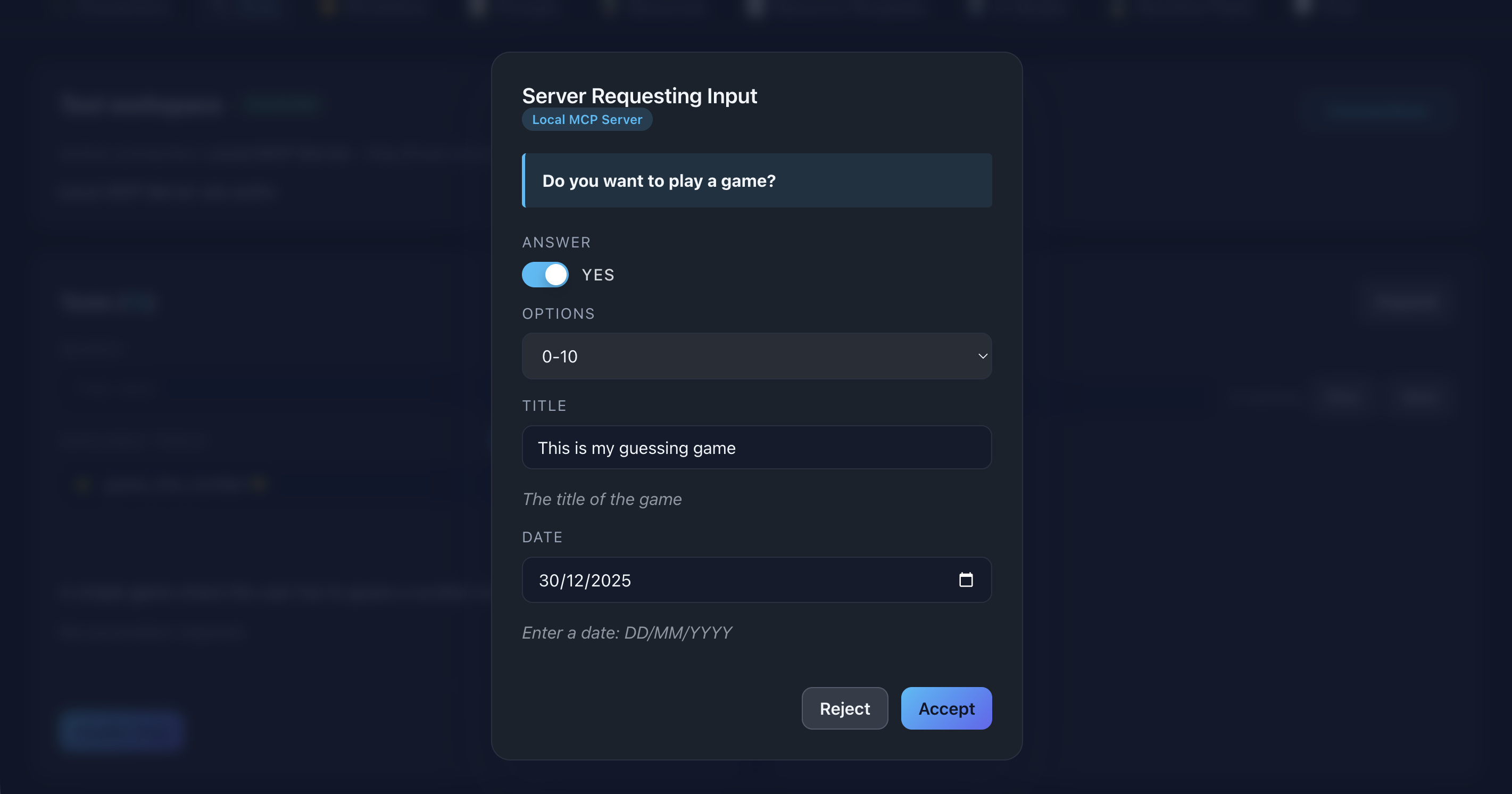
Description: Show examples of different string input types (date picker, email input, etc.) in an elicitation form
Enum
Display: Dropdown select with predefined options
Use case: Multiple choice selections
Example: Option (0-10, 11-20)
📸 Screenshot:
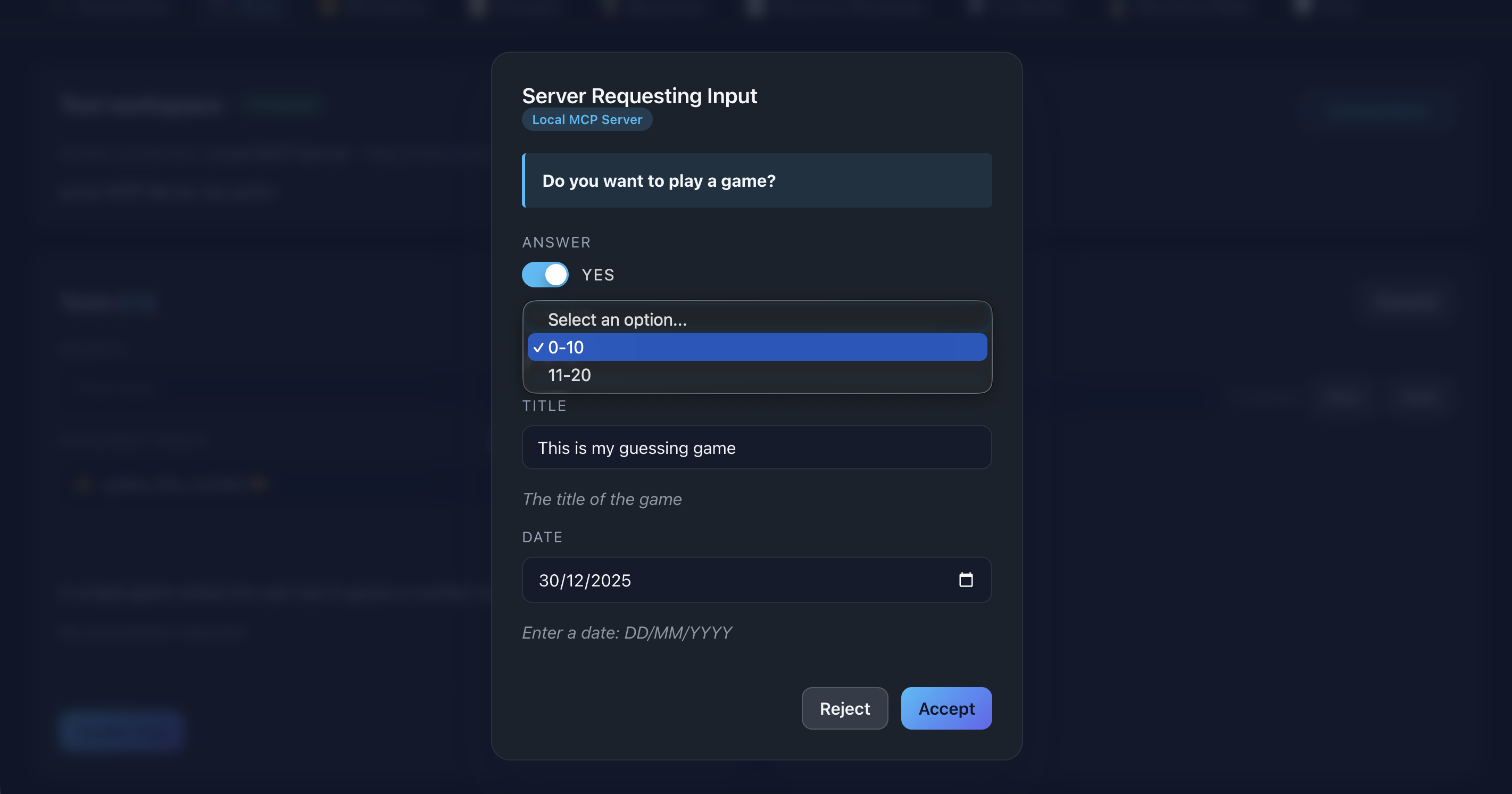
Description: Show an enum dropdown with multiple options in an elicitation form
Elicitations Tab
Navigate to 🤝 Elicitations tab to manage all requests.
Pending Requests
View all requests awaiting your response.
Displayed information:
- Connection name
- Server message
- Required input fields
- Accept/Reject buttons
How to respond:
- Fill in all required fields
- Click Accept to submit response
- Or click Reject to decline
📸 Screenshot:
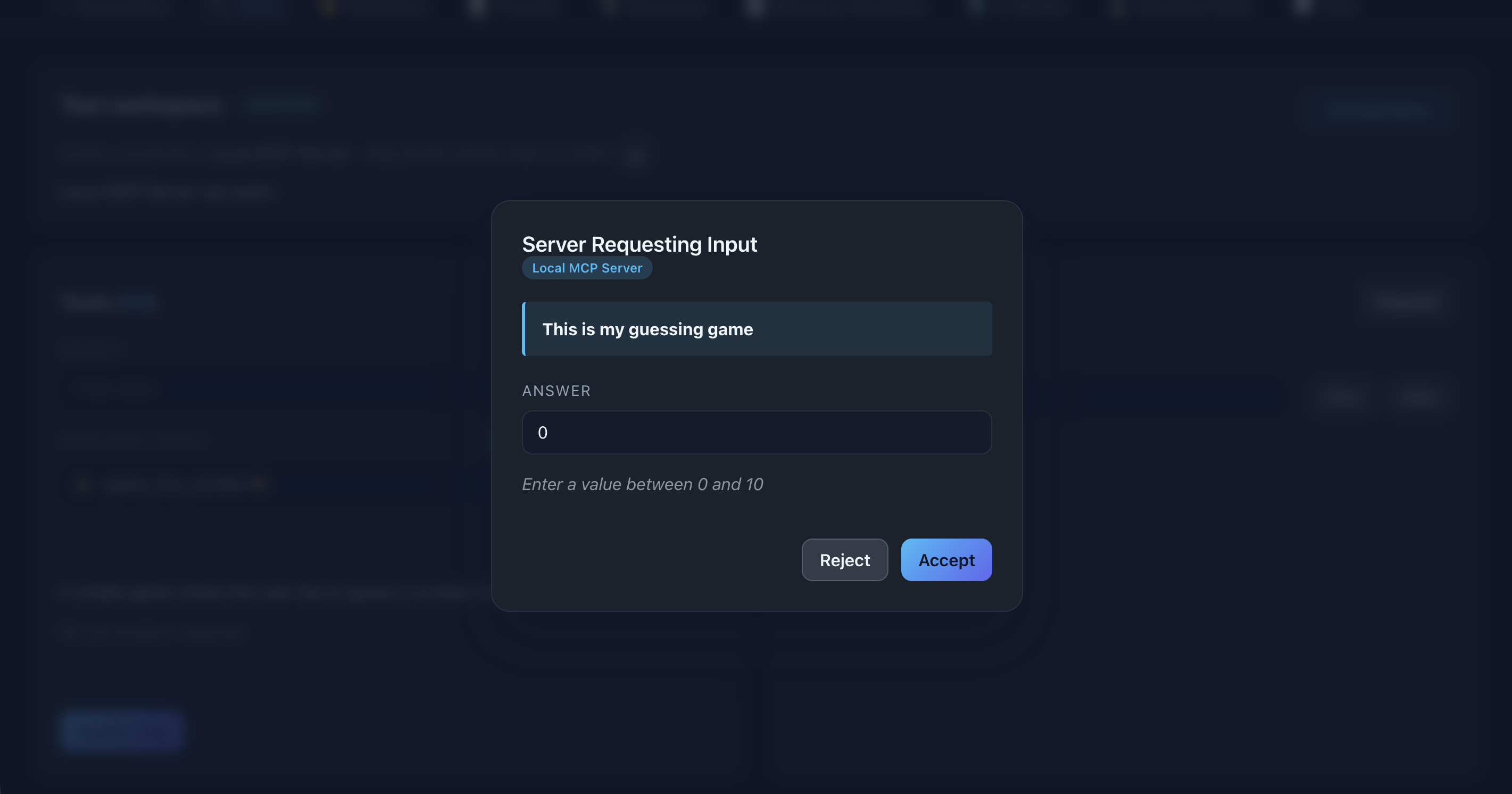
Description: Show the accepting the elicitation to progress it, then we see what values were entered
Screenshot:
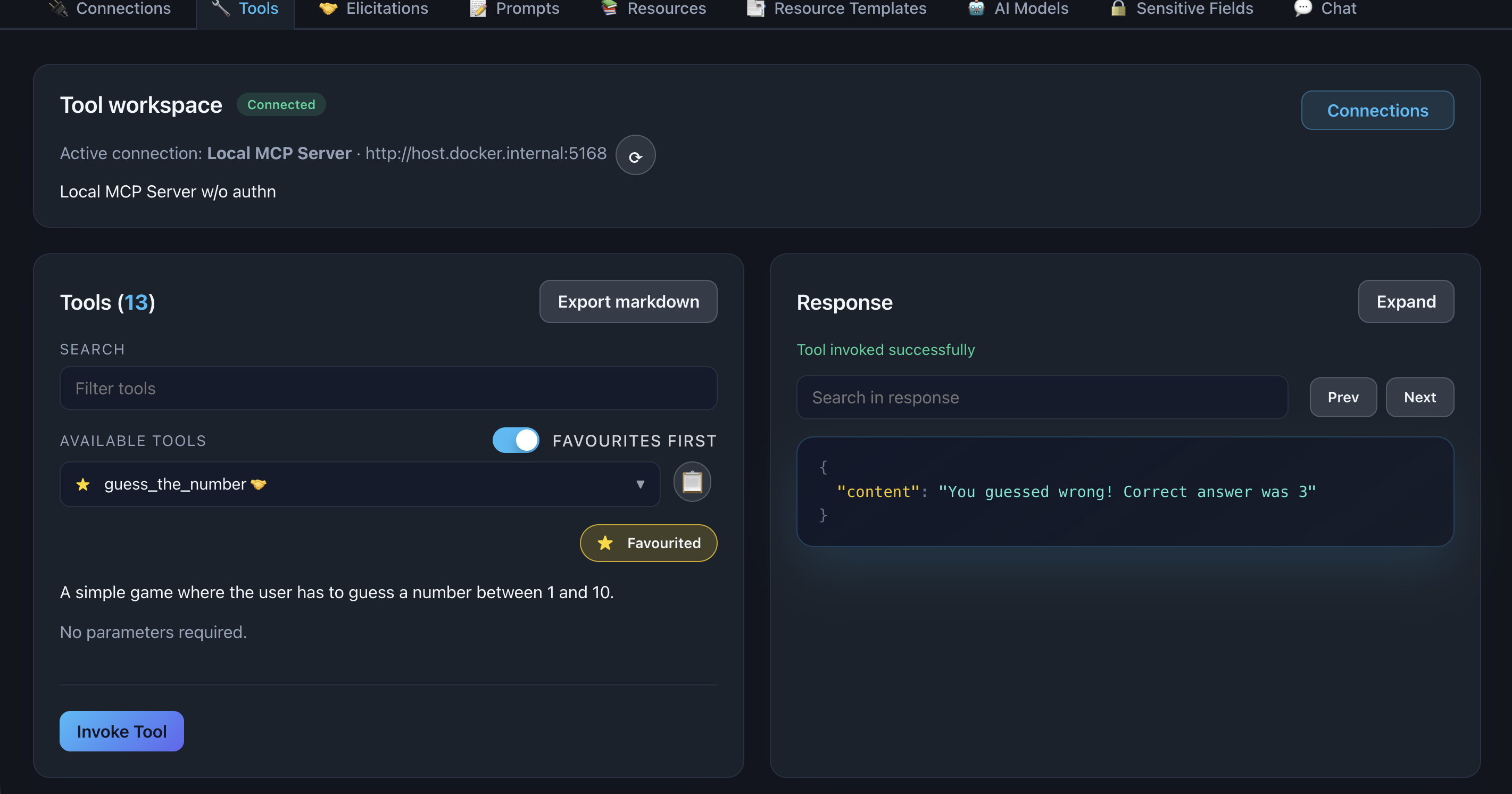
Description: Show the response from the tool after everything has been progressed through
History
Review all past elicitation requests.
Status badges:
- Pending (yellow): Awaiting response
- Accepted (green): User accepted and submitted values
- Rejected (gray): User declined or request timed out
Information shown:
- Timestamp
- Connection name
- Server message
- Status
- Submitted values (for accepted requests)
📸 Screenshot:
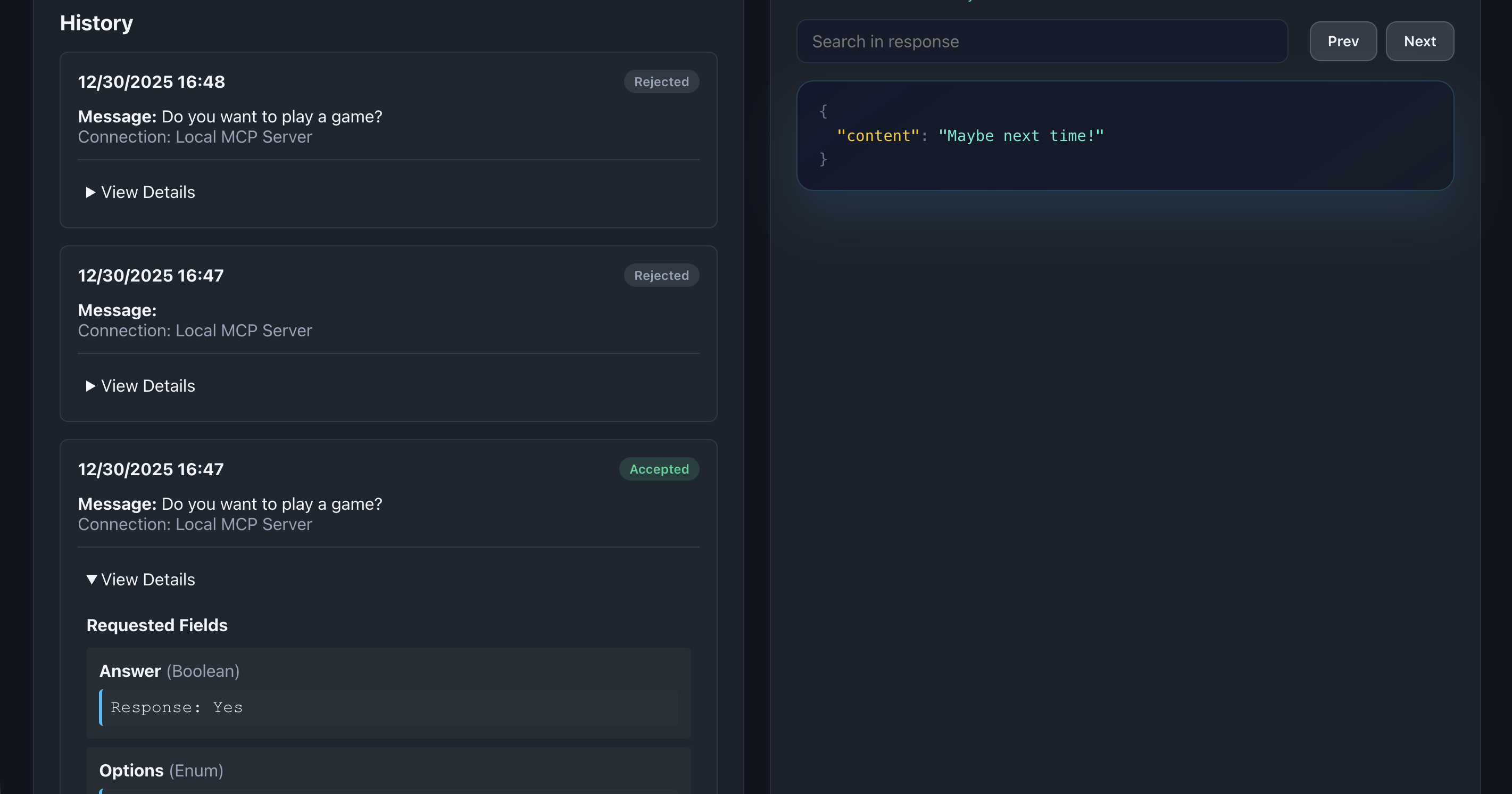
Description: Show the History section with multiple elicitations displaying different status badges
Configuration
Timeout Settings
Configure timeout behavior in appsettings.json:
{
"Elicitation": {
"TimeoutSeconds": 0
}
}
Values:
- 0 (default): No timeout, wait indefinitely
- Positive number: Timeout after N seconds, auto-reject
Use cases for timeout:
- Prevent indefinite hangs
- Enforce response time limits
- Automated workflows
Common Workflows
Approval During Tool Execution
- User calls a tool that requires approval
- Modal appears: “Approve deletion of 50 records?”
- User reviews and clicks Accept
- Tool continues and completes deletion
Multi-Field Data Entry
- Tool needs structured input (e.g., user profile)
- Modal shows multiple fields (name, email, age)
- User fills all fields
- Clicks Accept
- Server receives complete data object
Optional Rejection
- Modal appears with request
- User decides not to proceed
- Clicks Reject
- Server receives rejection response
- Tool execution halts or takes alternative path
Troubleshooting
Modal Doesn’t Appear
Solutions:
- Check that tool execution started
- Verify server supports elicitations
- Review console for errors
- Ensure browser allows modals
Input Validation Fails
Solutions:
- Check format requirements (email, URI, etc.)
- Fill all required fields
- Verify numeric values are valid numbers
- Check enum selection is from allowed values
Request Times Out
Solutions:
- Respond more quickly
- Increase
TimeoutSecondsin config - Set
TimeoutSeconds: 0for no timeout - Check if server enforces own timeout
Elicitation Implementation
Here’s a method that implements the elicitation shown in the screenshots above. You can find the original code ➡️ GuessTheNumber
Code extract
// uses a static readonly Random which is a better pattern for thread safety and randomness quality.
private static readonly Random _random = Random.Shared;
[McpServerTool]
[Description("A simple game where the user has to guess a number between 1 and 10. #elicitation")]
public async Task<string> GuessTheNumber(McpServer server, CancellationToken token)
{
// Ask if they want to play
var playResponse = await server.ElicitAsync(new ElicitRequestParams
{
Message = "Do you want to play a game?",
RequestedSchema = new ElicitRequestParams.RequestSchema
{
Properties =
{
["Answer"] = new ElicitRequestParams.BooleanSchema(),
["Options"] = new ElicitRequestParams.EnumSchema
{
EnumNames = new List<string> { "0-10", "11-20" }
},
["Title"] = new ElicitRequestParams.StringSchema
{
MaxLength = 30,
Description = "The title of the game"
},
["Date"] = new ElicitRequestParams.StringSchema
{
Description = "Enter a date: DD/MM/YYYY",
Format = "date"
}
}
}
}, token);
if (playResponse.Action != "accept" || playResponse.Content?["Answer"].ValueKind != JsonValueKind.True)
return "Maybe next time!";
// Get game parameters and ask for guess
var title = playResponse.Content?["Title"].GetString() ?? "Guess the number";
var useHighRange = playResponse.Content?["Options"].GetString() == "11-20";
var (min, max) = useHighRange ? (11, 20) : (0, 10);
_logger.LogInformation("Game title: {Title}, Range: {Min}-{Max}", title, min, max);
var guessResponse = await server.ElicitAsync(new ElicitRequestParams
{
Message = title,
RequestedSchema = new ElicitRequestParams.RequestSchema
{
Properties =
{
["Answer"] = new ElicitRequestParams.NumberSchema
{
Minimum = min,
Maximum = max,
Description = $"Enter a value between {min} and {max}"
}
}
}
}, token);
var guess = guessResponse.Content?["Answer"].GetInt32();
var correctAnswer = _random.Next(min, max + 1);
_logger.LogInformation("Guess: {Guess}, Correct answer: {Answer}", guess, correctAnswer);
return guess == correctAnswer
? "You guessed correctly!"
: $"You guessed wrong! Correct answer was {correctAnswer}";
}